Source: The Conversation – Canada – By Laura Misener, Professor & Director, School of Kinesiology, Western University
The verdict is in on the sexual assault trial of five former members of Canada’s 2018 world junior hockey team — all five have been acquitted.
Each player was accused of sexually assaulting a woman in a hotel room. Today, Justice Maria Carroccia stated that the Crown did not prove its case beyond a reasonable doubt.
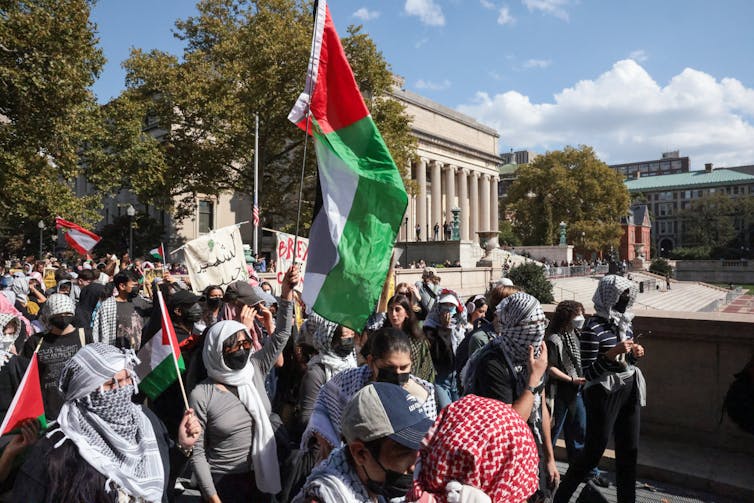
The trial has captured the world’s attention and sparked polarized public debates about consent, hockey culture and the role of sport in socializing young men.
Elite athletes often operate within environments where their talent grants them special status and access to resources — monetary and otherwise — that bolster a sense of entitlement. In some instances, sport organizations exacerbate this sentiment by protecting their star performers instead of addressing misconduct, which was reflected in this case.
For example, an abusive national vaulting coach for New Zealand Athletics was finally banned for 10 years, but only after years of unchecked abuse of his female athletes, including “inappropriate sexual references.” This highlights how misconduct can go on unrestrained for so long.
The culture of exceptionalism
As researchers with expertise in sport culture and sexual and gender-based violence, we’re reflecting on what the Hockey Canada trial reveals about the institutional and cultural practices within sport.
The formal and informal rules of men’s sport validate misogyny and reinforce systemic patterns of sexual entitlement and inadequate accountability. We offer some perspectives on how these troubling patterns of violence in sport can be reformed.
The Hockey Canada sexual assault trial has become a focal point for questioning how elite sporting environments shield athletes from accountability. This may be especially true in hockey.
In their book about toxic hockey culture, authors Evan Moore and Jashmina Shaw argue that hockey operates within “a bubble composed mostly of boys and men who are white, cis-het, straight and upper-class. And those who play often become coaches and teach the same values to the next generation.”
This closely knit community thrives on conformity and creates conditions that are ripe for the pervasive misogyny against women and systemic silence around issues of consent. The book _Skating on Thin Ice: Professional Hockey, Rape Culture and Violence against Women_, written by criminal justice scholars and sports reporters, demonstrates how endemic sexism, heavy alcohol use, abusive peers and the sexual objectification of women are buttressed by broader social factors. These factor uphold and reproduce toxic hockey culture, including patriarchal beliefs.
Male-dominated sporting cultures also emphasize a particular type of masculinity that focuses on dominance, physical intimidation and winning at all costs. This can blur the boundaries between acceptable competitive behaviour and problematic aggression.
Vulnerability in sports
Within the realm of professional sport, athletes also become commodified and objectified through media coverage, sponsorship deals and public scrutiny. This commodification can contribute to a culture where athletes may internalize the idea that their bodies are public property, further eroding their sense of autonomy and understanding of consent, especially in relation to others beyond the sport context.
Questioning or circumventing institutionally sanctioned behaviours is not easy, and it’s well-documented that many elite athletes struggle with mental health issues including depression, anxiety and substance misuse resulting from the pressure to align with the dominant culture.
But what often gets forgotten is how the hyper-masculine culture of sports creates significant barriers to seeking help. Young male athletes are socialized to comply with peer cultures that equate vulnerability with weakness. Yet they face intense pressures around family expectations, sponsorship deals and team success that demands they maintain appearances of strength and control.
This cycle of suppressed vulnerability and untreated distress enables toxic sporting masculinity to flourish, forcing organizations like Hockey Canada to confront their role in perpetuating these harmful dynamics.
The need for structural, cultural reform
Sports organizations have significant financial and reputational investment in athletes. This can create an inherent conflict when misconducts arise, problematically prompting sports organizations to use their power and resources to prioritize damage control over justice.
We saw this in the Hockey Canada sexual assault trial, where each hockey player had his own legal counsel, a stark illustration of institutional power and the extent to which sports organizations will go to shield their members from accountability. The deeply entrenched networks within sport prioritize self-preservation over addressing misconduct
Effectively responding to these issues requires addressing the systemic factors that perpetuate sexual and gender-based violence in sport. The sport ecosystem in Canada needs radical change, including who trains and mentors young men in hockey and how organizations investigate complaints.
It requires going beyond individual accountability, participating in consent workshops or issuing policy documents. These actions alone are insufficient to shift the cultural needle.
In 2022, Hockey Canada released a comprehensive action plan to address systemic issues in hockey that features discussions of accountability, governance, education and training and independent sport safety structures.
Community organizations like the Ontario Coalition of Rape Crisis Centres also issued a series of recommendations in 2022 that remain germane:
- Work with athletes and sports organizations to address sexual violence in sports culture;
- Support the development and growth of male allies programs within community-based sexual assault support centres; and
- Support those who have been harmed.
In addition to these excellent suggestions, Hockey Canada and other allied hockey organizations must be willing to restructure the current hierarchical structure of power that governs not just hockey, but also the players and all the other agencies involved, including coaches, sponsors, trainers, legal teams, media and PR representatives.
These organizational changes are possible, as evidenced by the efforts of Bayne Pettinger, an agent who has led efforts to create space for queer hockey players in Hockey Canada and the National Hockey League.

THE CANADIAN PRESS/Sean Kilpatrick
Sport’s moral reckoning
However, the cultural norms of power in sport extend beyond the playing field to shape attitudes toward consent and sexual conduct.
Until sport organizations address the foundational cultural elements that enable misconduct — toxic masculinity, institutional protection and erosion of consent culture — meaningful change will remain elusive.
Within hockey environments, in particular, the objectification of women and the institutional silence surrounding sexual violence have become normalized aspects of the sport’s culture, creating conditions where misconduct can flourish unchecked.
The events examined in this most recent trial are not isolated incidents but symptoms of deeper systemic failures within elite sport.
Only through comprehensive cultural transformation can we ensure that sport environments are spaces of genuine safety, respect and accountability for all participants.
![]()
Laura Misener receives funding from Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada
Treena Orchard receives funding from Western University for a Teaching Innovation Grant, however, those funds were not used in the creation of this article.
– ref. Hockey Canada sex assault verdict: Sports culture should have also been on trial – https://theconversation.com/hockey-canada-sex-assault-verdict-sports-culture-should-have-also-been-on-trial-260662