Source: The Conversation – USA (3) – By Güneş Murat Tezcür, Professor and Director of the School of Politics and Global Studies, Arizona State University

In July 2025, clashes between the Druze religious minority and Sunni Arabs backed by government-affiliated forces led to hundreds of deaths in Sweida province in southern Syria. Israel later launched dozens of airstrikes in support of the Druze.
This eruption of violence was an eerie reminder of what had unfolded in March 2025 when supporters of the fallen regime led by Bashar Assad, an Alawite, targeted security units. In retaliation, militias affiliated with the newly formed government in Damascus carried out indiscriminate killings of Alawites.
While exact figures remain difficult to verify, more than 1,300 individuals, most of them Alawites, lost their lives. In some cases, entire families were summarily executed.
Although the Syrian government promised an investigation into the atrocities, home invasions, kidnappings of Alawite women and extrajudicial executions of Alawite men continue.
The violence in Sweida also bore a sectarian dimension, pitting members of a religious minority against armed groups aligned with the country’s Sunni majority.
A key difference, however, involved the active Israeli support for the Druze and the U.S. efforts to broker a ceasefire.
Post-Assad Syria has seen promising developments, including the lifting of international sanctions, a resurgence of civil society and the end of diplomatic isolation. There was even a limited rapprochement with the main Kurdish political party controlling northeastern Syria.
The persistent violence targeting the Alawites and, to a more limited extent, the Druze, starkly contrasts with these trends. As a scholar of religious minorities and the Middle East, I argue that the current political situation reflects their historical persecution and marginalization.
History of the Alawites
The Alawites emerged as a distinct religious community in the 10th century in the region of the Latakia coastal mountains, which today make up northwestern Syria.
Although their beliefs have some commonalities with Shiite Islam, the Alawites maintain their own unique religious leadership and rituals. Under the Ottoman regime in the late 19th century, they benefited from reforms such as the expansion of educational opportunities and economic modernization, while gaining geographical and social mobility.
After Hafez Assad, the father of Bashar, came to power in a coup in 1970, he drew upon his Alawite base to reinforce his regime. Consequently, Alawites became disproportionately represented in the officer corps and intelligence services.
Prior to the civil war, which began in 2011, their population was estimated at around 2 million, constituting roughly 10% of Syria’s population. During the civil war, Alawite young men fighting for the regime suffered heavy casualties. However, most Alawites remained in Syria, while Sunni Arabs and Kurds were disproportionately displaced or became refugees.

AP Photo/Omar Albam
Among Syria’s minorities, two key factors make the Alawites most vulnerable to mass violence in post-Assad Syria. The first factor is that, like the Druze, Alawites have their own distinct beliefs that deviate from Sunni Islam. Their religious practices and teachings are often described as “esoteric” and remain mostly inaccessible to outsiders.
In my 2024 book “Liminal Minorities: Religious Difference and Mass Violence in Muslim Societies,” I categorize the Alawites and Druze in Syria alongside Yezidis in Iraq, Alevis in Turkey and Baha’is in Iran as “liminal minorities” – religious groups subject to deep-seated stigmas transmitted across generations.
These groups are often treated as heretics who split from Islam and whose beliefs and rituals are deemed beyond the pale of acceptance. For instance, according to Alawite beliefs, Ali, the son-in-law of Prophet Muhammad, is a divine manifestation of God, which challenges the idea of strict monotheism central to Sunni Islam.
From the perspective of Sunni orthodoxy, these groups’ beliefs have been a source of suspicion and disdain. A series of fatwas by prominent Sunni clerics from the 14th to the 19th century declared Alawites heretics.
Resentment against the Alawites
The second factor contributing to the Alawites’ vulnerability is the widespread perception that they were the main beneficiaries of the Assad regime, which engaged in mass murder against its own citizens. Although power remained narrowly concentrated under Assad, many Alawites occupied key positions in the security apparatus as well as the government.
In today’s political landscape where the central government remains weak and its control over various armed groups is limited, religious stigmatization and political resentment create fertile ground for mass violence targeting the Alawites.
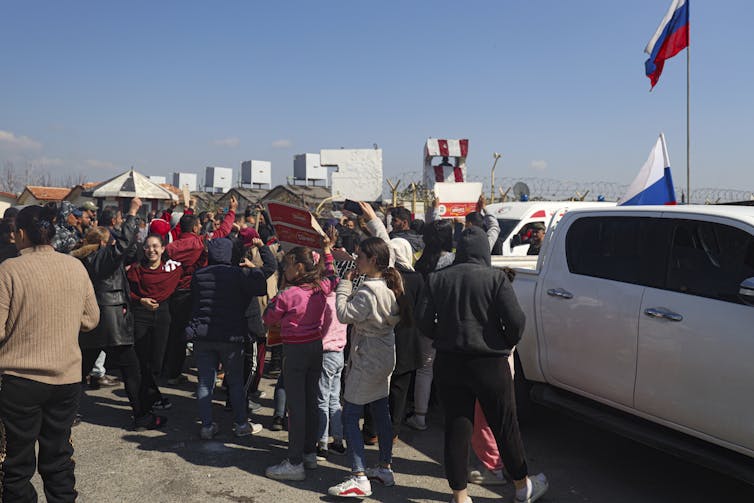
The massacres of March 2025 were accompanied by sectarian hate speech, including open calls for the extermination of the Alawites, both in the streets and on social media.
While many Sunni Muslims in Syria also perceive the Druze as heretics, they maintained a greater degree of distance from the Assad regime and were less integrated into its security apparatus.
Nonetheless, in recent months the situation deteriorated rapidly in the Druze heartland. The Druze militias and local Bedouin tribes engaged in heavy fighting in July 2025. Unlike the Alawites, the Druze received direct military assistance from Israel, which has its small but influential Druze population. This further complicates peaceful coexistence among religious groups in post-Assad Syria.
A sober future
Sunni Arab identity is central to the newly formed government in Damascus, which can come at the expense of religious and ethnic pluralism. However, it has incentives to rein in arbitrary violence against the Alawites and Druze. Projecting itself as a source of order and national unity helps the government internationally, both diplomatically and economically.
Internally, however, the new government remains fractured and lacks effective control over vast swaths of territory. While it pays lip service to transitional justice, it is also cautious about being perceived as overly lenient toward individuals associated with the Assad regime and its crimes. Meanwhile, Alawite and Druze demands for regional autonomy continue to stoke popular Sunni resentments and risk triggering further cycles of instability and violence.
I believe that in a post-Assad Syria defined by fractured governance and episodic retribution, the Alawites as well as Druze are likely to face deepening marginalization.
![]()
Güneş Murat Tezcür does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
– ref. Understanding the violence against Alawites and Druze in Syria after Assad – https://theconversation.com/understanding-the-violence-against-alawites-and-druze-in-syria-after-assad-255292